What is a 6-Axis Robot?
Since its invention in 1973 with the introduction of the KUKA FAMULUS, the humble 6-axis industrial robot has transformed the manufacturing sector.
The flexibility of modern industrial robot systems has helped factories reduces labor cost and optimize their manufacturing processes to improve speed & efficiency. At the heart of the automation revolution’ are six-axis robots.
What is a 6-axis robot? What are the common applications for these industrial robot systems? What are 6-axis collaboration robots? How much do 6-axis robots cost?
In this article, we’ll explain all you’ll need to know about 6-axis robots and how to implement them in your industrial processes.
What is a 6-Axis Robot?
6-axis robots refer to articulated robots – i.e. industrial robot systems containing rotary joints – that have six axes (or degrees of freedom).
In simple terms, each degree of freedom describes a possible range of motion in one direction of motion.
When a robot has six degrees of freedom, it is able to move freely in six directions (or axes). This represents the entire range of motion for a static object in a 3D space.
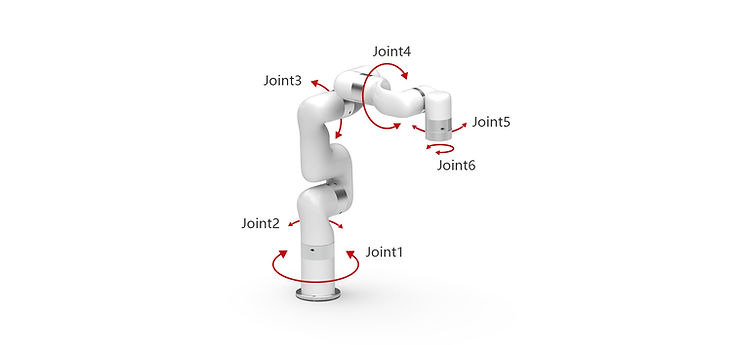
How is each of these six axes defined? They are:
Joint 1: The robot can swivel horizontally at the base. In an industrial robot, this degree of freedom is used to change the direction of the arm from left to right without extending the arm itself.
Joint 2: This degree of freedom involves the extending and retracting of the lower arm. This provides the robot with the ability to move forwards and backwards.
Joint 3: This axis provides the robot with the ability to move up and down. This is achieved by raising or lowering the joint between the two sections of the robot’s arm.
Joint 4: This degree of freedom describes the ability to rotate the upper arm from left to right. This is used to change the orientation of an object attached to the arm’s end effector through rolling motion (as opposed to the yaw movement of the 5th axis.
Joint 5: Combined with the 4th-axis, this degree of freedom also helps adjust the positioning of an object attached to the arm’s end effector. This axis however controls the yaw positioning of the object by lifting and lowering the arm’s end effector.
Joint 6: The final degree of freedom involves rotating the arm’s end-effector. This provides pitch movement capability.
When compared to industrial robot systems with fewer degrees of freedom – for example, cartesian, SCARA or delta robots – six-axis robots offer a far more flexible range of motion and thus applications.
Effectively, 6-axis robots can simulate the entire range of motion offered by a human arm. This allows these robots to effectively replace human operatives in many industrial tasks – all while offering much greater strength, speed and dexterity.
The additional range of motion allows a six-axis robot to complete complex tasks and manoeuvres, such as welding, machine tending and palletizing. This reduces labor and operating costs, increases efficiency and helps industrial firms bring products to market faster.
What is a 6-axis collaborative robot?
A collaborative robot is a type of 6-axis industrial robot system that includes extra safeguards and features to make them safe for operation around humans. Collaborative robots are used for human-robot collaborative processes.
Traditional industrial robot systems are primarily designed for robot-only processes – where they operate far away from any humans. Given the strength and speed of 6-axis robots, they present a significant safety hazard on factory floors.
However, modern factories found that certain tasks along an industrial pipeline are best suited for skilled human workers. The space needed around traditional 6-axis robots for safe operation made it difficult to introduce this.
Collaborative robots are lighter and include proximity sensors to detect when their arm is about to collide with a person and shut down motion. These machines don’t need to be divided by barriers, unlocking some unique human-robot workflows.
Home appliance manufacturer Whirlpool first adopted collaborative robots in 2015. The corporation’s automation lead Eric Howe justified the move by saying:
“Collaborative robots allow us to be much more flexible. They also are easier to program than traditional robots, which saves time. The addition of the robots allows our employees to focus on tasks that require greater cognitive skill.”
Common Applications: What are 6-axis robots used for?
6-axis robots have allowed industrial firms to automate tasks that would otherwise need skilled operatives to complete. The ability to replicate the full range of motion of the human arm helps here – but the added strength and speed of 6-axis robots opens new possibilities for industrial applications.
Here are some of the most exciting uses for 6-axis robots:
Screwdriving & Part Insertion: 6-axis robots can automate the assembly of components and products. The accuracy in movement of these robotic systems allows them to quickly complete screwdriving and part insertion tasks, allowing them to assemble anything from toys and small gadget to appliances or even cars.
Glueing: These robotic systems can safely automate glueing materials together. Hot adhesive can severely burn your worker’s hands, and therefore replacing this task can mitigate a significant safety risk. Firms also tend to see an improvement in the cleanliness of adhesive applications using robots, with neater glueing and less residue found.
Painting: 6-axis robots are ideal for spraying and painting intricate products. Paint sprays can easily be attached to an arm’s end connector. By programming paint sprays, firms can ensure a perfect paint application every time.
Sanding & Polishing: In the same vein, sanding and polishing tools can be attached to robot arms to automate these processes. This automation can help guarantee consistent, high-quality finishes.
Packaging & Palletizing: This highly repetitive task is most effectively completed by automated robots. 6-axis robots ensure that products are packed correctly, reducing the likelihood of damage in shipping.
How much does a 6-axis robot cost?
Given the design and construction complexity of these robotic systems, 6-axis robots are usually more expensive than traditional robots.
However, the efficiency and production workflow gains afforded by the versatile robots mean industrial firms regularly see significant returns on investment (ROI) implementing 6-axis robots.
What factors influence the price of 6-axis robots? These include:
-
Robot arm cost
-
End-of-arm tools cost
-
Sensor cost
-
Mounting tool cost
-
Software cost
-
Integration cost
-
Maintenance cost
-
Shipping cost
-
Technical support cost
Many 6-axis robot manufacturers regularly charge upwards of $25,000 for each robot. For example, Mitsubishi Electric prices their 6-axis robotics solutions between $25,000-$35,000. Both ABB and Doosan offer robots for upwards of $50,000.
However, newer manufacturers like Ufactory offer far more competitive options for growing industrial firms. We provide the most affordable collaborative robots on the market.