A robotic arm is a common feature in the modern industrial workplace. This mechanized and programmable human-like arm can execute heavy-duty and constantly repeated tasks quickly and with great precision. The unique structure of a robotic arm dictates its specific application. You will know four parts of the robot arm in this article:
What is a robot arm?
What are the parts of a robot arm?
Different Types of Robotic Arms?
How to choose A Right robot?
What is A Robot Arm?
A robot arm is a programmable human-like arm designed to execute rigorous, energy-intensive and highly repetitive tasks quickly and efficiently. It is used in industries to carry out jobs which will otherwise not be done by humans. This includes activities that require high levels of precision. A robot arm can fit a cap on beverage bottles with an equal amount of force, even if it is made to do so a thousand times; humans won’t be able to do this. This modus operandi of a robotic arm is a reflection of the root word of ‘robot’; robota—a Czech word which means forced labor.
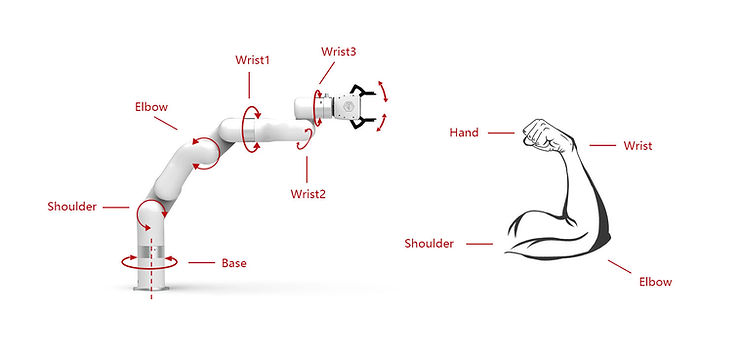
The structural plan of the typical robot arm consists of seven segments and six joints. This structural framework makes it very similar to the human arm though its shoulder is connected to a stationary base. Also, it allows it to exhibit a range of movements. While the human arm permits movement in seven planes, the typical robot arm permits movement in six planes. The segments and joints of a robot arm interact to produce movements. At each joint, motors are installed. The computer moves the robot arm by rotating the motors. The movement of motors is in discrete steps producing more precise movements which are reproducible.
A robot arm operates based on the command issued to it. A programmer can teach a robot arm how to do a particular task by walking it through the different steps involved. A handheld controller is used to guide the arm through the different patterns of movement. Once the robot arm has fully assimilated the routine and stored it in its memory, it can execute the same pattern of movements again and again with the same level of precision.
One area where robot arms find great application is in manufacturing. A recent survey shows that approximately 45% of industrial production can be mechanized using robotics. According to Cobot Intel, industrial robot arms are used in the automobile industry for coupling cars and in the computer industry for putting together tiny microchips.
The proliferation of robot arms in the workplace can be attributed to reduced production costs and advancements in its technology. A combination of these factors has made robotic arms readily available and affordable. This means their use is not only limited to large-scale production but also small-scale operations. In both cases, robot arms serve to boost product output.
It is important to be safety conscious when working with industrial robots. This is in light of the speed and intensity at which robot arms function. As Cobot Intel rightly put it, industrial robots are designed to be operated in a controlled manner.
What Are The Parts Of A Robotic Arm?
The different parts of a robotic arm are arranged to make it resemble a human arm, having a shoulder, elbow and wrist.
A typical robot arm contains two parts, one is the arm (manipulator), another is the controller (motion planning system).
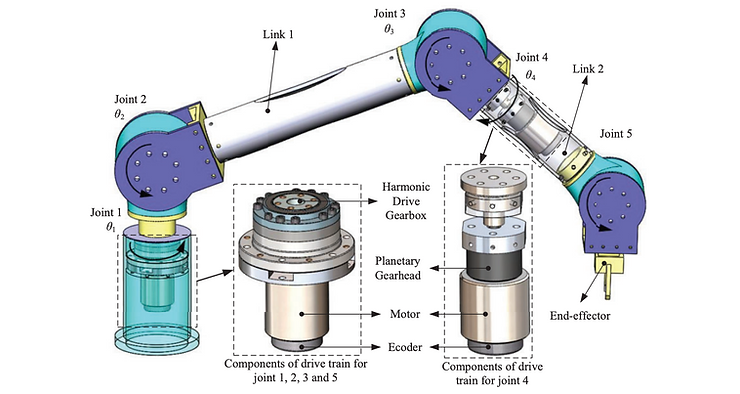
Haibin Yin, A unified design for lightweight robotic arms based on unified description of structure and drive trains, July 2017 International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems 14(4):1
Arm
The arm is also described as a manipulator. This is the part of the robot that functions to execute tasks. The arm helps to align the end effector in the right position. It consists of four main components, namely:
Gearbox
This component is responsible for controlling the speed and direction of movement. It is also the key to guarantee the lifetime and accuracy. It acts as an interface between the motor, which generates mechanical energy for a planned movement, and the end effector, which carries out the eventual movement. It is the guarantee of the robot’s lifecycle.
A common gearbox type is the harmonic drive, also called strain wave gearing or zero backlash gearbox. They are light-weight, space saving and durable, which are born to produce very high-precision outcomes.
Servo Motor
This is the main power source of robots. The servo motor is specialized for high-response, high-precision positioning. As a motor capable of accurate rotation angle and speed control, it can be used for a variety of equipment.
A servo motor has a rotor which is set into rotary motion by a servo drive. It also has an inbuilt sensor which provides information about velocity and position of the rotor to the servo drive. The servo drive uses this information to regulate the movement of the rotor. The Servo motor is well adapted for use in high-precision applications as well as high-speed operations.
Motor drivers
Their function, as their name implies, is to upgrade low-current signals to high-current signals powerful enough to drive the servo motor. The electric circuit present in the servo motor operates on low currents, which is not sufficient enough to drive it. Hence the need for motor drivers.
In addition, they ensure precise robot control. For instance, an absolute encoder, which is the key to get the position feedback of the motor driver, informs the servomotor of the position when the robot arm is turned on. This prevents errors in instances when there’s an unexpected power outage; the servomotor has to be aware of the position before it can recommence work.
Links
Links serve as rigid structures that constitute the mechanism of the robot. They equip the robotic arm with the stiffness required for quick and accurate operations. Carbon fiber is an ideal material for robots. Compared with aluminum, carbon fiber has great thermal stability. In addition, it doesn’t affect the accuracy of the robot. Its light weight saves power, ensures a longer work time and makes the workflow safer. However, considering the production cost, most robots are built with aluminum.
Controller
The controller functions to oversee the different parts of a robotic arm. It consists of two major components. They include:
Robot brain
This is the part of the controller that receives instructions, interprets and executes them. It processes the command and plans the trajectory by dedicated algorithm. There are 2 basic parts of the algorithm:
Inverse kinematics: here, the robot utilizes kinematic equations to calculate the motion required to reach a specific position.
Forward kinematics: here, the robot uses angular velocities and joint angles to determine both the velocity and position of end effectors.
Usually, it needs a x86 high-performance processor which is powerful enough to process the position of each actuator inside the robot arm thousands of times in each second.
User Interface
This is an important aspect of a robotic controller. It ensures easy handling of the robot. This is the component that allows users to send commands to the robot. The common form of this feature is a teach pendant. A teach pendant is hand-operated and tablet-like. It is used by programmers to teach the robot arm how to perform a task. The teach pendant is removed when the robot arm is ready to be deployed, but here is a more convenient way, you can use a tabletop or an iPad to control the UFactory robot anytime.
Robotic controllers ensure a smooth workflow. They are used to control both simple work processes and complex manufacturing procedures. The controller determines the ease with which a robotic arm executes a task. The effectiveness of a robot arm is largely dependent on the controller.
Sensor
This component provides information about the robotic arm and its surrounding. Robotic arm sensors act just like our human senses. Sensors enable a robot arm to see, hear, taste, touch and smell. An industrial robot can detect a noxious smell helping to safeguard against chemical leakage. Robotic sensors include:
Internal sensors
They provide information about the robot’s position, acceleration, velocity and torque.
A collision detector sensor is a basic equipment of a robot arm. It helps the robot arm avoid collisions by helping to detect an object in its path.
External sensors
They capture information about the robot’s surroundings. This external data include the layout of the environment. An external sensor collects all this information and relays it back to the controller. This feedback is then used by the controller to fine-tune the movements of the end effector. External sensors include:
Force torque sensor
Helps the robot arm to know what’s going on in all axes.
Visual Sensors
The sense of vision is the most commonly utilized robotic sense. Visual sensors can provide a view of the environment. A visual sensor helps an industrial robot to know which item to pick out of a number of items. The functionality of an optical sensor is immense. A visual sensor can identify an object’s color, assess the thickness of a material, determine the smoothness of a surface and measure a liquid’s flow rate. An optical sensor can provide information about the position and velocity of a robot arm.
A visual sensor can be in form of a camera or a laser scanner.
Visual sensors powered by laser utilize Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) and can be applied in both 2D and 3D. The laser technology allows for quick and precise measurement of distance. The laser scanner measure distances by estimating the time lapse between the emitted electromagnetic pulse and reflection from the nearest object. A shorter time lapse means the object is nearby, while a longer time lapse indicates a farther object. Laser-powered optical sensors have their limitations. Their vision can be clouded by direct sunlight. Notwithstanding, laser sensors exhibit more resistance to direct sunlight compared to other sensors.
The robotic visual sense has been greatly improved. Autonomous robotic arms are no longer limited by obstacles. The visual acuity of cameras is much better. Optical sensors can now differentiate between a human and an object. High-speed software has been introduced for the swift processing of visual data obtained by optical sensors.
For improved accuracy and reliability, robot arms obtain data using a combination of sensors.
End effector
This component can be likened to the hand in a human arm. It is the robotic part that’s in contact with the object to be manipulated. It can be in the form of a 2-finger gripper, BIO gripper, magnet, welder gun, drill and vacuum pump. This is an important part of a robot arm. It is the component that makes a robot arm ideal for a particular task. End effectors make it possible to customize a robot arm for a specific role easily. It just requires that you swap the end effector with another that is best suited for the new task. With the aid of end effectors, a robotic arm can be made to be multifunctional. The same robot that bores holes can also tighten bolts.
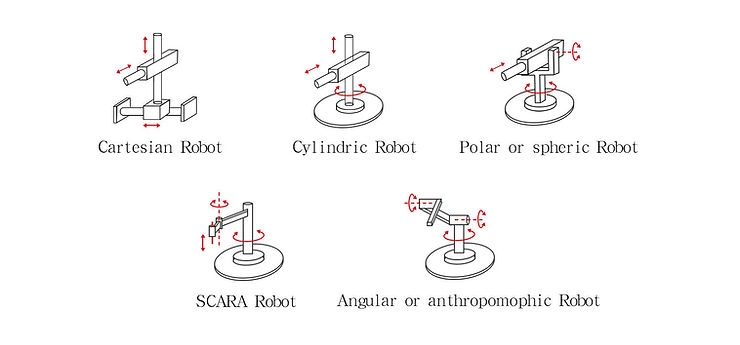
Different Types of Robotic Arms